By CNBCTV18.COM of Mar 17, 2022
The Big Four Accounting firms are Deloitte, PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC), Ernst & Young, KPMG
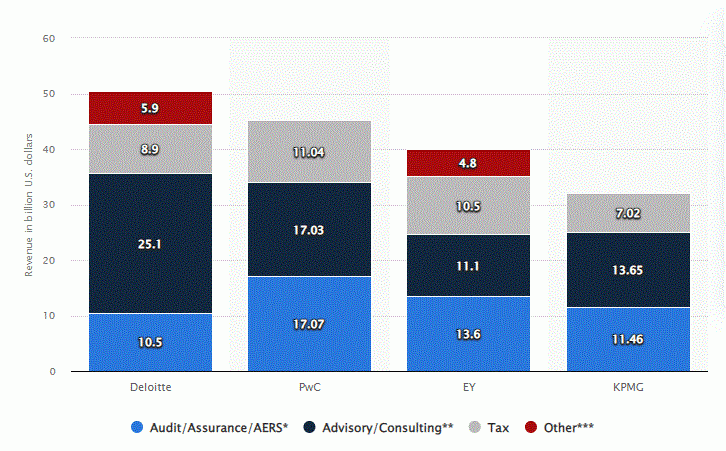
Revenue of the Big Four accounting / audit firms worldwide in 2021
The investigation is part of the The United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)’s campaign to shore up regulatory compliance from accountants, bankers and lawyers. As these entities are the line of communication between the companies and investors, it is important for their integrity to be maintained.
“You will see that we will have a firm commitment moving forward to continue to target deficient auditing by auditors, auditor independence cases, cases around earnings management,” Gurbir Grewal, SEC Enforcement Director, had said at the national conference of auditors in December.
Why are the four firms being investigated?
Under SEC rules, accounting and auditing firms are barred from conducting any services for clients that would cause impairment in their auditing and accounting duties to ensure that auditors remain objective and impartial in their findings. In this regard, the SEC had sent out notices to Deloitte & Touche LLP, Ernst & Young LLP, KPMG LLP, and PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP; the four biggest accounting companies in the world, asking for information about services being given to clients that may potentially violate the above rule.
While other smaller firms also received letters from the SEC, the Big Four, as they’re known, audit 66 percent of all public companies in the US. Analysis from Audit Analytics also found that 47 of the S&P500 companies paid significant non-audit fees, amounting to more than 25 percent of the total fees paid, to the accounting firms. These non-audit services include consulting, tax advice, and lobbying to audit clients.
Not the first time
This is not the first time that the Big Four have been in the crosshairs of the SEC. All four companies have faced similar actions in the past.
PwC had paid nearly $8 million to the SEC to settle a case regarding a violation of audit-independence rules in 2019. EY has settled twice with the SEC in the past seven years regarding investigations alleging it violated independence rules, paying $4 million in 2014 and $10 million last year. KPMG in the same year had paid $8.2 million to the SEC to settle an investigation into its alleged violations. Deloitte also paid $1.1 million to settle an SEC enforcement action in 2015. EY, KPMG and Deloitte settled their cases without admitting or denying any wrongdoing. PwC also settled their cases without admitting or denying any wrongdoing but agreed to be suspended from auditing financial statements of public companies for four years.
1.Deloitte
Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Limited commonly referred to as Deloitte, is an international professional services network headquartered in London, United Kingdom.
The firm was founded by William Welch Deloitte in London in 1845 and expanded into the United States in 1890. It merged with Haskins & Sells to form Deloitte Haskins & Sells in 1972 and with Touche Ross in the US to form Deloitte & Touche in 1989. In 1993, the international firm was renamed Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu, later abbreviated to Deloitte. In 2002, Arthur Andersen‘s practice in the UK as well as several of that firm’s practices in Europe and North and South America agreed to merge with Deloitte. Subsequent acquisitions have included Monitor Group, a large strategy consulting business, in January 2013. The international firm is a UK private company, limited by guarantee, supported by a network of independent legal entities.
Deloitte provides audit, consulting, financial advisory, risk advisory, tax, and legal services with approximately 334,800 professionals globally. In FY 2021, the network earned revenues of US$50.2 billion in aggregate. As of 2020, Deloitte is the third-largest privately-owned company in the United States, according to Forbes. The firm has sponsored a number of activities and events including the 2012 Summer Olympics.
Cases
Controversies involving the firm, in addition to litigation surrounding a few of its audits, have included its involvement in a “potentially misleading” report on illicit tobacco trading in Australia, the fact that it suffered a major cyber-attack which breached client confidentiality as well as exposing extensive employee information in September 2017, its role as internal auditor of the insolvent contractor Carillion and its role as external auditor of Autonomy which was accused of “accounting improprieties” that contributed to an £8.8 billion write-down of value following its acquisition by Hewlett-Packard in 2011.
2.PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC)
The firm in its recent actual form was created in 1998 by a merger between two accounting firms: Coopers & Lybrand, and Price Waterhouse. Both firms had histories dating back to the 19th century. The trading name was shortened to PwC (stylized pwc) in September 2010 as part of a rebranding effort.
PricewaterhouseCoopers International Limited, based in London, England, is a co-ordinating entity for the global network of firms. It manages the global brand, and develops policies and initiatives, to create a common and coordinated approach in areas such as risk, quality, and strategy. It does not provide services to clients
It is the second-largest professional services network in the world and is considered one of the Big Four accounting firms. PwC firms are in 157 countries, across 742 locations, with 284,000 people. As of 2019, 26% of the workforce was based in the Americas, 26% in Asia, 32% in Western Europe and 5% in Middle East and Africa. The company’s global revenues were $42.4 billion in FY 2019, of which $17.4 billion was generated by its Assurance practice, $10.7 billion by its Tax and Legal practice and $14.4 billion by its Advisory practice.
3.Ernst & Young
Ernst & Young Global Limited, trade name EY is a multinational professional services partnership headquartered in London, England
It primarily provides assurance (which includes financial audit), tax, consulting and advisory services to its clients. Like many of the larger accounting firms in recent years, EY has expanded into markets adjacent to accounting, including strategy, operations, HR, technology, and financial services consulting.
EY operates as a network of member firms which are structured as separate legal entities in a partnership, which has 312,250 employees in over 700 offices in more than 150 countries around the world. Revenue in 2021 US$ 40 billion
The firm’s current partnership was formed in 1989 by a merger of two accounting firms; Ernst & Whinney and Arthur Young & Co. It was named Ernst & Young until a rebranding campaign officially changed its name to EY in 2013, although this initialism was already used informally prior to its sanctioning adoption.
In 2019, EY was the seventh-largest privately owned organization in the United States. EY has continuously been ranked on Fortune magazine’s list of the 100 Best Companies to Work For for the past 21 years, longer than any other accounting firm
4.KPMG
KPMG International Limited (or simply KPMG) is a multinational professional services network, and one of the Big Four accounting organizations. Revenue in 2021 US$ 13 Billion
Headquartered in Amstelveen, Netherlands, although incorporated in the United Kingdom, KPMG is a network of firms in 145 countries, with over 236,000 employees and has three lines of services: financial audit, tax, and advisory. Its tax and advisory services are further divided into various service groups. Over the past decade various parts of the firm’s global network of affiliates have been involved in regulatory actions as well as lawsuits.
The name “KPMG” stands for “Klynveld Peat Marwick Goerdeler”. The initialism was chosen when KMG (Klynveld Main Goerdeler) merged with Peat Marwick in 1987.
posted by gandatmadi46@yahoo.com

Looking great work dear, I appreciated you for this quality work. Nice post!! these tips may help me in future